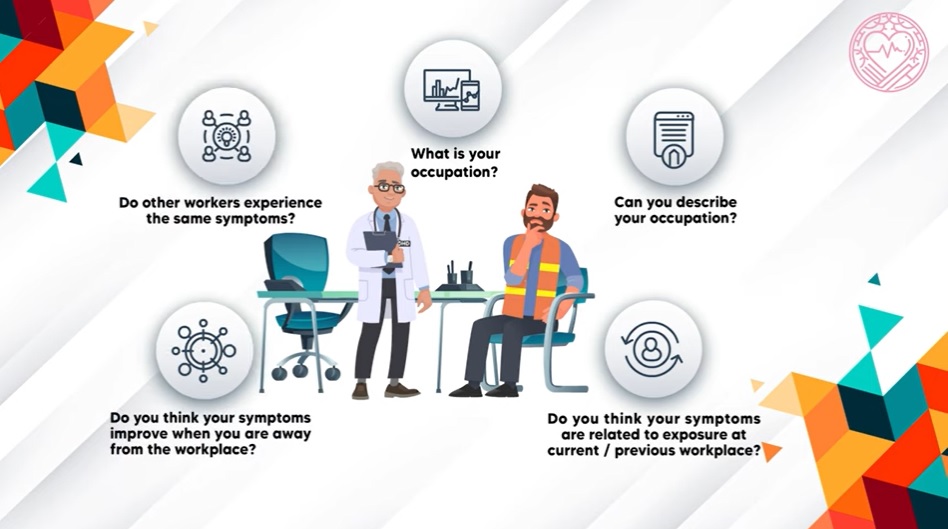
Taking care of liver health
The Star Online, 25 May 2014

Although fatty liver disease is often associated with alcohol consumption, nondrinkers are also at risk, especially those who are obese. – shutterstock/AFP
Addressing myths about liver disease.
THE liver is one of the largest and most important organs in the body. It is located in the upper right portion of the abdomen and is involved in many vital processes.
Some of the functions of the liver include:
· Converts the food you eat into energy and produces chemicals your brain and spinal cord need.
· Controls the production and excretion of cholesterol.
· Helps fight infections by producing immune factors and removing bacteria from the blood.
· Controls blood clotting.
· Filters and neutralises drugs, alcohol and environmental toxins that enter the body.
· Stores vitamins, minerals and sugars, and releases them in the blood when your body needs them.
· Regulates fat stores.
There are many preconceived notions, misconceptions and myths about liver disease. Knowing the facts and dispelling the harmful myths can be your key to a healthy life.
Myth: I should feel pain when my liver is unwell.
In the early stage of liver disease, your liver may become inflamed.
However, unlike most other parts of the body that become hot and painful when inflamed, an inflamed liver may not cause any discomfort at all.
Liver inflammation can slowly worsen, causing scarring or fibrosis.
As fibrosis worsens, cirrhosis develops, and the liver becomes seriously scarred, hardened and unable to function properly.
By the time you experience symptoms such as jaundice, your liver would have been severely damaged.
Myth: Victims of liver disease are alcoholics.
Liver disease is not a disease specific to alcohol drinkers. There are more than 100 causes of liver disease.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, a disease of the liver not associated with excessive or prolonged alcohol consumption, is the most common cause of abnormal liver tests in the US.
Certain groups of people are recognised as having an increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, especially those who are obese, those who have diabetes, and those with high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides (fats) in their blood.
Myth: Alcohol can damage the liver only when taken in excess.
Alcohol is harmful to the liver, so any amount can produce damage to the liver.
Myth: Stopping alcohol intake when one has advanced liver disease is useless.
Even in advanced liver disease, it is still beneficial to stop drinking alcohol. Studies show that people with advanced liver disease (cirrhosis) who continue drinking have only a 33% chance of surviving for five years compared to 65% of those who stopped.
Myth: Fatty liver only affects fat people.
Thin people or those of average build can also get fatty liver. People can develop fatty liver even if they do not have health problems such as diabetes or obesity.
Regardless of build, people can get fatty liver from an unhealthy lifestyle that causes fat deposits to build up in their liver cells.
Myth: I am a healthy adult. I don’t have to worry about liver problems.
Liver problems can strike anyone, from infants to seniors. Liver disease can be hereditary, caused by toxic substances, viruses and bacteria, or a complication of an unhealthy lifestyle.
One of the first signs of liver damage is fatty liver, a condition characterised by the accumulation of fat in liver cells.
Beware fatty liver
In general, fatty liver is reversible if caught early and the cause is treated (e.g. stop drinking alcohol, treat metabolic syndrome). However if it progresses and the liver is inflamed, it can lead to permanent damage.
Fatty liver is commonly associated with alcohol intake or metabolic syndrome (diabetes, hypertension, obesity and high cholesterol), but can also be due to any one of many causes.
If the issue of fatty liver is not addressed, the condition can progress to cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver. The most common causes are alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis infection and fatty liver. Other causes include toxins (e.g. certain medications) and autoimmune disorders.
Sadly, cirrhosis cannot be cured, but progression of the disease can be slowed down by treating the cause, e.g. taking antiviral medications, maintaining a good diet, not drinking any alcohol.
Tips on liver care
The liver takes care of your overall health, but it also depends on you to take care of it so that it can do its job properly.
Here’re some tips on how to do this:
Eat right – Eat a balanced diet rich in different types of vegetables, fruits and proteins. Avoid excess fats and carbohydrates as they can cause fat deposits in the liver. Eat smaller meals as they are easier to digest and are less of a burden to the liver.
Avoid alcohol – Drink moderately or stop altogether. This covers beer, wine, cocktails, champagne and liquor in any other form.
Do not abuse drugs – Even seemingly harmless medicines can damage the liver. Follow your doctor’s prescribed treatment strictly. Do not indulge in recreational drugs.
Avoid environmental pollutants – When using insecticides and sprays, make sure the room is well-ventilated, or wear a suitable mask.
Beware of herbal supplements – Be careful what you take. Not everything “natural” is safe. Some herbal remedies are reported to cause liver toxicities.
Observe practices that lessen the risk of infection to the liver – Wash your hands properly after using the toilet and before eating, practise safe sex and consider vaccination for viral hepatitis.
Stay active – Exercise regularly to increase muscle mass and reduce body fat. There is good evidence that gradual weight loss coupled with increased exercise will help reduce fat deposits in the liver.
De-stress regularly – Make time for hobbies, meditation, tai chi, yoga or whatever that helps you relax and unwind. The less stress on you, the less stress on your health, including your liver.
Consider liver supplements – Consult your doctor if you have concerns about your liver health. Essential phospholipids (EPLs) may help. Phospholipids are the building blocks of all body cells, including that of the liver. They are a class of lipids (fats) that serve an extremely important function in the body. When the cell membrane loses phospholipids, it is said to be damaged and the function of the cell is weakened. Severe damage to the cell membrane can kill the cell and affect the vital functions of the organ.
Your body can produce some types of phospholipids, but others must be supplied by your diet. Phospholipids that can only be obtained through dietary intake are called “essential phospholipids”.
This article is courtesy of Essentiale.

























 >
>